Unlock Your IoT Devices: SSH Remote Access Tips & Free Download Insights
Managing your Internet of Things (IoT) devices can feel a bit like overseeing a busy, sprawling network, especially when they are scattered in different places. You want to make sure they are running smoothly, that their data is safe, and that you can check on them anytime, anywhere. This is where SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, really comes into its own for remote access to your IoT gadgets. It offers a secure way to connect, letting you send commands and manage things from afar, so you can keep everything in order without needing to be right next to each device.
So, you might be wondering how this whole SSH thing works for tiny computers and sensors. Well, it's pretty simple: SSH sets up an encrypted link between your computer and your IoT device. This means any information you send back and forth is kept private and safe from prying eyes. It's almost like having a secret, secure pathway directly to your device, giving you peace of mind that your commands and data are protected. This is particularly important for devices that might be in public spaces or handling sensitive information, you know?
This article will walk you through the key aspects of using SSH for your IoT devices. We will cover everything from setting up secure connections with special keys to figuring out why your connection might freeze. We'll even look at how to automate tasks on your devices, making your life a little easier. You will also get some insights into what "free download" typically refers to when we talk about SSH tools, which are usually readily available for anyone to use. By the end, you should feel much more confident about keeping your IoT world connected and secure.
Table of Contents
- Understanding SSH for IoT Devices
- The Importance of SSH Keys for IoT Security
- Troubleshooting Common SSH Connection Issues
- Automating IoT Tasks with SSH Scripts
- Setting Up SSH for Your IoT Device: A Quick Look
- What "Free Download" Means for SSH and IoT
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
- Bringing It All Together: Your IoT and SSH Connection
Understanding SSH for IoT Devices
When you connect to an IoT device using SSH, you are tapping into a very reliable way to communicate. As a matter of fact, the "ssh://" part you might see in a clone URL or connection string tells you that you are connecting via the SSH protocol. This protocol is built on strong security principles, which is really important for devices that might be out in the open or handling data that needs to stay private. It's a bit like having a secure phone line directly to your device, so only you can hear what's being said, or rather, what commands are being sent.
Every device you connect to using SSH, you know, has its own unique key. This "host key" is like a digital fingerprint for that device. Your SSH client, the program you use to connect, remembers this host key. This means that the first time you connect to a new device, your client will ask you to confirm its key. Once you say "yes," your client keeps that key on file, and for future connections, it checks to make sure the device you are connecting to is indeed the one you think it is. This simple check adds a layer of trust and helps prevent someone from pretending to be your device, which is quite a good thing for security.
For example, if you have a small IoT sensor running Linux and you need to check its status or update its software, SSH is your go-to tool. You can open your terminal, type a simple command, and just like that, you are logged in, able to run commands as if you were sitting right in front of the device. This capability is, in a way, what makes remote IoT management not just possible, but also very practical and secure. It's pretty cool how much control you get from anywhere.
The Importance of SSH Keys for IoT Security
Using SSH keys for your IoT devices is a huge step up from relying on passwords alone. Think of it this way: instead of typing a password every time, which could potentially be guessed or intercepted, you use a pair of cryptographic keys. One key, the public key, lives on your IoT device, and the other, the private key, stays safe on your computer. When you try to connect, these two keys work together to prove who you are, without ever sending your private key over the network. This method is much more secure and, frankly, a lot more convenient once it's set up.
Creating and Managing Your SSH Keys
Creating these keys is a straightforward process, usually done right in your terminal. You can generate a public and private key pair with a single command. Once you have them, you will need to copy your public key to your IoT device. A common way to do this is to use a command like `pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub` on your local machine, which copies your public key to your clipboard. Then, you can paste it into the `~/.ssh/authorized_keys` file on your IoT device. This setup allows your device to recognize your computer, letting you connect without a password, which is a very handy feature for automation and security.
It's also worth noting that keeping your private keys secure is absolutely critical. They are, after all, the digital equivalent of your house keys. If someone gets hold of your private key, they could potentially gain access to your IoT devices. So, make sure they are stored in a safe place on your computer, perhaps with a strong passphrase protecting them. Some people use tools like `keychain` to manage their SSH identities, which helps persist them across sessions. This means you do not have to type your passphrase over and over again, which is quite convenient.
Using Specific Keypairs for Different Connections
You might find yourself needing to connect to various SSH proxy servers or different IoT devices, each with its own specific security needs. In such cases, using a unique SSH keypair for each connection, rather than your default `id_rsa` keypair, is a good idea. This practice, you know, adds another layer of security. If one key is compromised, it does not affect your access to other devices or services. For instance, someone might have created a specific keypair just for a particular proxy server, which is a smart way to manage access control.
This approach is particularly useful in work environments where you might have different levels of access for various systems. You could have one key for your development IoT devices, another for production ones, and perhaps a third for a specific server that hosts a PostgreSQL database, like the one running on Ubuntu server 14.04 mentioned in "My text". This separation helps keep things organized and secure. It is, in a way, like having different sets of keys for different doors, each providing access to a specific area.
Troubleshooting Common SSH Connection Issues
Even with the best setup, you might run into a few bumps along the road when connecting to your IoT devices via SSH. It's pretty common, actually. Sometimes, connections freeze, or certain features do not work as expected. Knowing how to diagnose these problems can save you a lot of time and frustration. We'll go through some common scenarios and how to approach them, drawing from real-world experiences.
Dealing with Terminal Freezes
One of the most annoying issues is when your terminal just freezes during an SSH session. You are connected, everything seems fine, and then suddenly, nothing. This can happen for a few reasons, such as network instability or an issue on the remote device itself. In "My text," someone experienced their "terminal freezes in 10" (seconds or minutes, it's not specified, but the frustration is clear). If your connection usually works perfectly when you are in the workplace, but then freezes when you are somewhere else, it might point to a network problem, like a firewall blocking certain traffic or a less stable internet connection. Sometimes, simply restarting your SSH client or checking your network connection can help. It's often a good first step, honestly.
Checking for X11 Forwarding Problems
If you are trying to run graphical applications from your IoT device on your local machine, you will need X11 forwarding. This allows the display output from the remote device to show up on your computer. If you run an SSH command and your display is not set, it means SSH is not forwarding the X11 connection. To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, you can check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output of your SSH connection attempt. If that line is missing, you might need to enable X11 forwarding in your SSH client configuration or on the remote IoT device itself. This is a pretty common thing to overlook, but easily fixed once you know what to look for.
Understanding Host Key Verification
We touched on this earlier, but it is worth revisiting. Your SSH client remembers the host key associated with a particular server or IoT device. This is a security feature to protect you from "man-in-the-middle" attacks, where someone might try to impersonate your device. If the host key changes unexpectedly, your client will warn you. This usually happens if you reinstall the operating system on your IoT device, or if you connect to a new device that happens to have the same IP address as a previous one. While it can be a bit startling, it's a good sign that SSH is doing its job. You just need to verify the new key or remove the old one from your known hosts file, which is a simple command to run, really.
When Remote Scripts Return Errors
Sometimes, you might run a script on your remote IoT device via SSH, and it just returns an error code like "255." As "My text" points out, "For some reason your remote script returns 255, and ssh just delivers its result to you." This means the script itself had an issue, and SSH is simply reporting its exit status. SSH is just the messenger here. To figure out what went wrong, you really need to look at the script itself. "How about showing us the script?" is a valid question in such a scenario, as the problem is almost certainly within the script's logic or the environment it is running in on the IoT device, not with SSH itself. Debugging these scripts often involves adding logging or running parts of the script manually to pinpoint the exact failure point, which is a bit like being a detective.
Automating IoT Tasks with SSH Scripts
One of the truly powerful things you can do with SSH for your IoT devices is automate tasks. Instead of manually logging in every time to run a command, you can write scripts that do the work for you. This is incredibly useful for routine maintenance, data collection, or even triggering actions based on certain conditions. Someone in "My text" was "writing a script to automate some command line commands in python," which is a perfect example of this. They had commands like `Cmd = "some unix command"` that they wanted to run automatically.
Imagine you have a fleet of IoT sensors, and you need to update their software every month. Instead of connecting to each one individually, you could write a Python script that uses SSH to connect to each device, run the update command, and then disconnect. This saves a tremendous amount of time and reduces the chance of human error. It's a very efficient way to manage multiple devices, making your IoT setup much more scalable. You could, for instance, have a script that fetches data from Git repositories on your IoT devices, as mentioned in "My text" about "fetching or pulling from git repositories, or cloning a repository." This kind of automation is a game-changer for large-scale deployments.
When you are automating, it is crucial to make sure your SSH connections are passwordless, using those SSH keypairs we talked about. This allows your script to connect without needing human intervention to type a password, which is essential for true automation. If you find yourself needing to fix things on multiple devices, like running "the following command (for each repo)" as described in "My text" from Git's instructions, an automation script can handle that for you seamlessly. This is where the true value of `ssh remote iot device free download` really shines, letting you manage your devices with minimal effort once the initial setup is done.
Setting Up SSH for Your IoT Device: A Quick Look
Getting SSH up and running on your IoT device typically involves a few key steps. First, you need to make sure your device has an SSH server installed and running. Many Linux-based IoT operating systems, like Raspberry Pi OS, come with an SSH server pre-installed or it is very easy to add. Then, you will configure it to allow connections, perhaps disabling password login in favor of SSH keys for better security. This is a pretty standard practice, honestly.
For example, if you have an IoT device running Ubuntu Server 14.04, much like the server with PostgreSQL 9.3 mentioned in "My text," you would first ensure the `openssh-server` package is installed. Once that is done, you can usually SSH into the server via your terminal without much fuss. The challenge often comes when trying to use graphical tools, like configuring PgAdmin III to do remote database management, as also noted in "My text." While direct terminal SSH works, these graphical applications might require additional setup, like proper X11 forwarding or specific connection settings within the application itself, which can be a bit tricky to get just right.
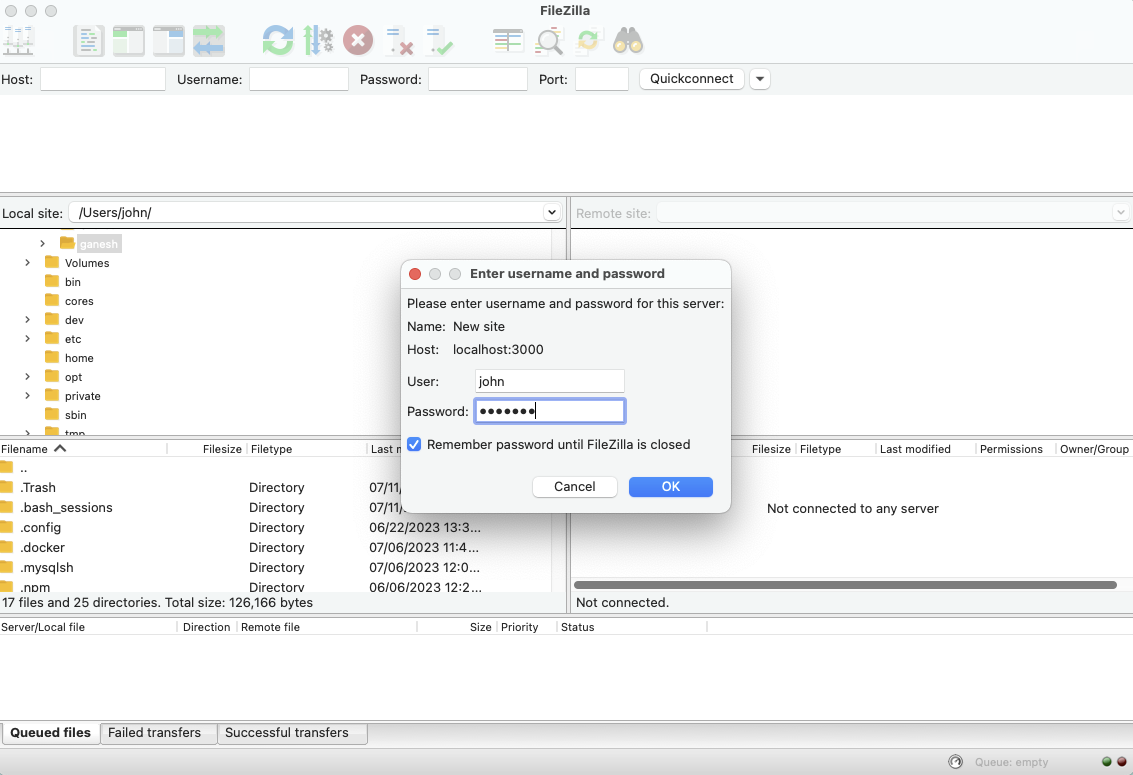
Remember, the goal is to establish a secure and reliable channel. This means not only setting up the SSH server on your IoT device but also ensuring your local machine, your client, is properly configured. This includes managing your SSH keys and understanding how to use them with various tools, whether it is a simple terminal command or a more complex file transfer client like FileZilla. As someone in "My text" found, trying to access a server using FileZilla often requires "authentication with public/private keys," which means you need to know where your keys are and how to point the client to them, especially if you "created the keys using the terminal, but cannot find them on my" system. Keeping track of your keys is quite important.
What "Free Download" Means for SSH and IoT
When you see "ssh remote iot device free download," it typically refers to the availability of SSH client software and related tools that are free to acquire and use. The SSH protocol itself is an open standard, meaning its specifications are publicly available, and there are many open-source implementations. This is a really big deal because it means you do not have to pay for expensive licenses to secure your IoT communications. It's almost like getting a professional-grade security tool for free, which is very helpful for hobbyists and large-scale deployments alike.
For instance, if you are using a Linux or macOS computer, an SSH client is usually pre-installed, so you do not even need to download anything extra. For Windows users, popular free options like PuTTY or the built-in OpenSSH client (available in modern Windows versions) are readily available. These tools allow you to establish those secure connections to your IoT devices. They are, in a way, your gateway to managing your devices remotely. The "free download" aspect makes SSH highly accessible to anyone looking to secure their IoT projects, from a single Raspberry Pi to a network of smart home sensors. This widespread availability helps foster innovation and security across the IoT ecosystem, which is a good thing for everyone, you know?
Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
Here are some common questions people ask about using SSH with their IoT devices:
How do I set up SSH on my Raspberry Pi for remote access?
Setting up SSH on a Raspberry Pi is quite straightforward. First, ensure SSH is enabled, which you can do through the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool or by creating an empty file named `ssh` in the boot partition of your SD card before booting the Pi. Then, you will need to find your Pi's IP address on your network. From your computer, you can then use a command like `ssh pi@your_pi_ip_address` in your terminal. For better security, it is highly recommended to set up SSH key-based authentication rather than relying on passwords, as this is much more secure and convenient for regular access.
What should I do if my SSH connection to my IoT device keeps disconnecting?
If your SSH connection frequently drops, several factors could be at play. Network instability is a common culprit; check your Wi-Fi signal or Ethernet connection on both ends. Sometimes, the remote IoT device might be running out of memory or CPU resources, causing it to become unresponsive. You can try increasing the SSH client's keep-alive settings to send periodic "heartbeat" signals, which can prevent idle connections from timing out. Also, check the logs on your IoT device for any errors or warnings that might indicate what is causing the disconnections, which can be very informative.
Is it safe to use SSH for my IoT devices over the internet?
Yes, using SSH for your IoT devices over the internet is generally considered safe, provided you follow best practices. SSH itself encrypts all traffic, protecting your data from eavesdropping. However, you must secure your SSH server on the IoT device. This means using strong, unique SSH keypairs instead of passwords, disabling root login, and changing the default SSH port from 22 to a non-standard one. Additionally, consider setting up a VPN or using a firewall to limit access to your SSH port to only trusted IP addresses. This layered approach adds significant protection for your devices, which is quite important for internet-facing systems.
Bringing It All Together: Your IoT and SSH Connection
As we have seen, SSH offers a powerful and secure way to manage your IoT devices from anywhere. From understanding the core protocol to mastering SSH keys and troubleshooting common issues, you have many tools at your disposal. The ability to automate tasks through scripts, as someone did with their Python commands, can transform how you interact with your devices, making management far more efficient. This is particularly useful for those moments when you are trying to connect to a server, perhaps to manage a PostgreSQL database, and find that direct terminal access works but a graphical tool like PgAdmin III struggles. Knowing how to check for issues like X11 forwarding problems or understanding why a remote script might return an error code like 255 puts you in a much better position to resolve things quickly.
The "free download" aspect of SSH tools makes this powerful technology accessible to everyone, from individual hobbyists to large organizations. It means you can get started without any financial barrier, focusing instead on the security and functionality of your IoT setup. Remember that managing your host keys, understanding why your terminal might freeze, and knowing how to use specific keypairs for different connections are all pieces of the puzzle. For more insights on securing your remote connections, you can learn more about the SSH protocol on our site. Also, if you want to explore more about remote access, you can link to this page . It's all about making your IoT journey smoother and more secure, you know?
Remote IoT Monitoring On Android: Free Download & SSH Guide
IoT SSH Remote Access - SocketXP Documentation
SSH Remote IoT Device Android: A Comprehensive Guide