Troubleshooting: Why Your Raspberry Pi VNC Access Over The Internet Isn't Working Today
It can feel pretty frustrating, can't it, when you're trying to get to your Raspberry Pi from somewhere else, maybe across town or even further, and VNC just won't connect. You've set up your little computer, perhaps for a home automation project, or maybe it's running a useful server, and you really need to get in there. When you're looking to access something important, like managing your smart home gadgets or checking on data, a non-working connection is a real headache. It's a bit like trying to use a city's access vehicles that are radio dispatched and ADA accessible, but the radio isn't working; you just can't get where you need to go. You want that smooth, dependable connection, and it's frustrating when it's just not there, you know?
Many folks, you see, want to control their tiny Raspberry Pi computers remotely. It makes sense, as a matter of fact. Whether it's to tweak some settings, run a quick command, or just see what's happening on its desktop, being able to connect from anywhere is super handy. You want to organize, analyze, and utilize what your Pi is doing, much like you'd want to with important information. This remote access, typically through VNC (Virtual Network Computing), lets you see and control your Pi's graphical interface as if you were sitting right in front of it. Yet, when you try to access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working, it can feel like hitting a brick wall, and that's just a little annoying.
This problem, where you can't get your Raspberry Pi's VNC working over the internet, is actually quite common. There are many moving parts involved, from your Pi's own settings to your home network, and even your internet provider. It's not always a simple fix, but usually, with a bit of patience and some methodical checking, you can figure out what's going on. We're going to walk through the common reasons why this happens and give you some clear steps to get things running smoothly again, so you can easily find just the data you want with your Pi, just like you would with a well-made database.
Table of Contents
- Understanding VNC and Remote Access
- Common Reasons VNC Fails Over the Internet
- Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
- Advanced Tips for Reliable Remote Access
Understanding VNC and Remote Access
VNC, which stands for Virtual Network Computing, is a system that allows you to control a computer from a distance. It's like having a window into your Raspberry Pi's desktop, no matter where you are. You can move the mouse, type on the keyboard, and see everything that's happening on the screen. It's a very convenient way to interact with your Pi without needing a monitor, keyboard, or mouse directly connected to it, which is pretty neat.
When you want to access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working, it means you're trying to reach your Pi from outside your home network. This is different from connecting when you're on the same Wi-Fi network at home. To make this work, information has to travel from your remote computer, through the vast internet, find your home network, and then specifically find your Raspberry Pi. It's a bit of a journey for the data, you know, and there are several points where things can get stuck, which is what we're here to figure out.
Common Reasons VNC Fails Over the Internet
There are quite a few reasons why your VNC connection might not be going through when you're trying to reach your Raspberry Pi from afar. It could be something simple, or it could be a combination of things. We'll look at the most frequent culprits, so you can systematically check each one. This methodical approach is often the best way to solve these kinds of problems, very much like how you'd organize and analyze data to find what you want with Microsoft Access.
Network Configuration Hurdles
Your home network, with its router and firewall, is the first line of defense and also the gateway to your Pi. If these parts aren't set up just right, your VNC connection won't ever make it to your Raspberry Pi. This is where many people run into issues, as network settings can be a little tricky to get a handle on, you see.
Port Forwarding Explained
Think of your router as a busy post office. When you try to connect to your Raspberry Pi from the internet, you're sending a letter to your home's address. But inside your home, you have many devices, each with its own "apartment number" (an internal IP address) and a specific "door" (a port number) that VNC uses, typically 5900 or 5901. Your router, the post office, needs to know exactly which device and which door that incoming VNC "letter" is meant for. This is what port forwarding does: it tells your router to send incoming traffic on a specific port (like 5900) to a specific internal IP address (your Raspberry Pi's IP) and port. If this isn't set up correctly, your router won't know where to send the VNC traffic, and it'll just drop it, which is a common reason why you might find your access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working. It's a very crucial step, actually.
To set this up, you'll need to log into your router's administration page. The address for this is usually something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but it can vary. You'll then look for a section called "Port Forwarding," "NAT," or "Virtual Servers." Here, you'll create a new rule. You'll specify the external port (e.g., 5900), the internal IP address of your Raspberry Pi (which needs to be static, more on that later), and the internal port (also 5900 for VNC). Make sure you save these changes. It's a bit like giving your post office a very specific instruction for a very specific delivery, and if it's not quite right, the letter won't get through, you know?
Router Firewall Settings
Most routers have a built-in firewall. This firewall is there to protect your home network from unwanted intrusions from the internet. While port forwarding opens a specific "door" for VNC traffic, sometimes the router's firewall might still be blocking it. You might need to check your router's firewall settings to ensure it's not overly restrictive. Some routers have a "high security" mode that blocks almost everything, and you might need to adjust this or add an exception for the VNC port. This is less common than incorrect port forwarding but can still be a reason your access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working. It's worth a look, just in case.
ISP Blocking and Double NAT
Sometimes, your internet service provider (ISP) might be the one causing trouble. Some ISPs block certain ports to prevent misuse or to simplify their network management. While port 5900 is generally not blocked, it's a possibility, especially if you're trying to use less common ports. You could try changing the external port you forward to something higher, like 20000, and then forwarding that to 5900 on your Pi. Another issue is "Double NAT." This happens when you have two routers in your network, perhaps one from your ISP and your own personal router connected to it. Each router performs Network Address Translation (NAT), and this double layer can make port forwarding very difficult or even impossible without additional configuration on both routers. You'd essentially have to port forward twice, which is a bit of a hassle, to be honest.
Raspberry Pi Configuration Glitches
Even if your network is perfectly set up, your Raspberry Pi itself needs to be ready to accept VNC connections. Small errors in its setup can prevent you from getting in. This is where you might need to get your hands dirty with a few commands on the Pi itself, but it's usually pretty straightforward, you know.
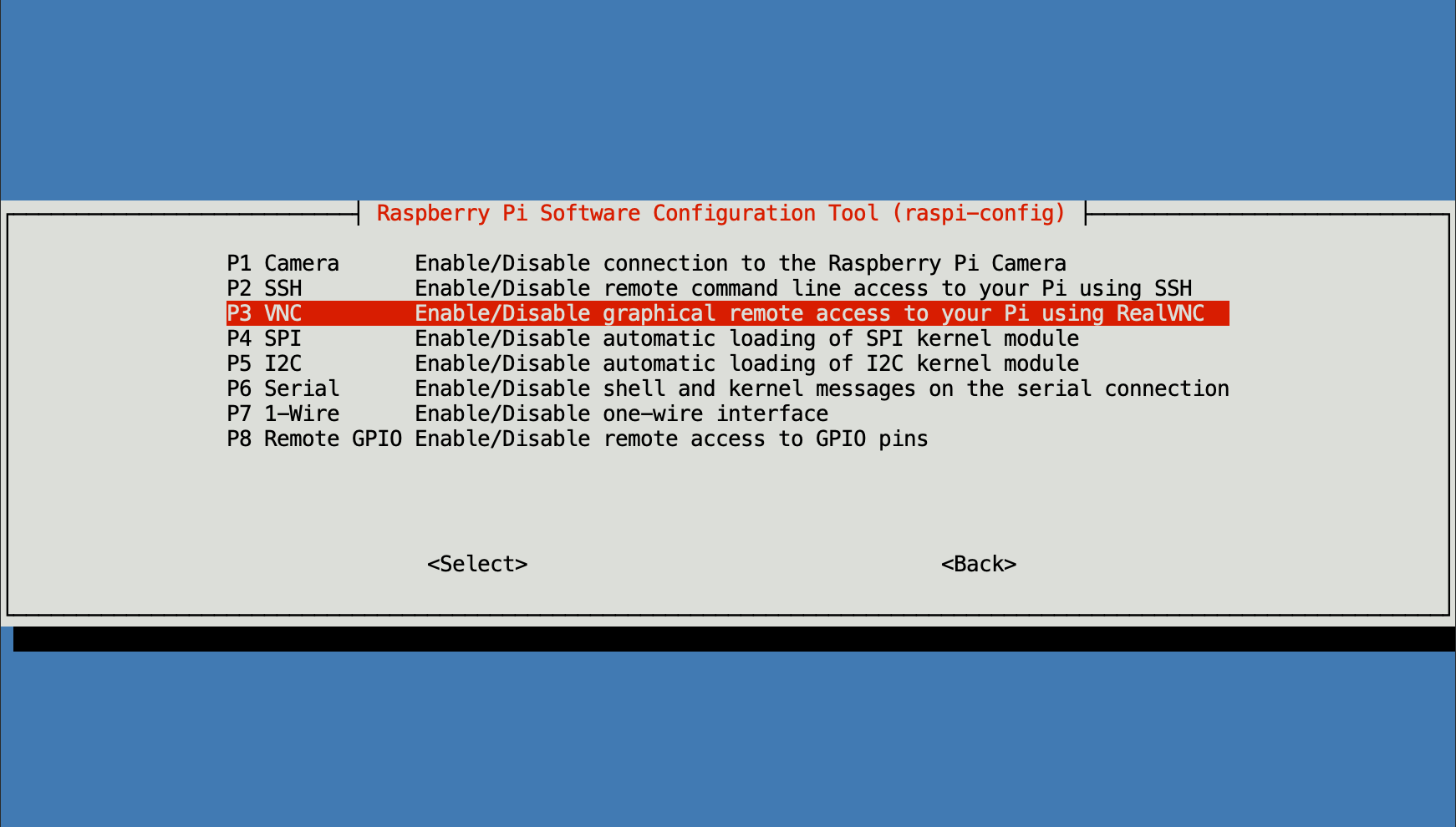
VNC Server Not Active
It sounds simple, but sometimes the VNC server software on your Raspberry Pi just isn't running. Maybe it crashed, or it didn't start automatically after a reboot. You need to make sure the VNC server (like RealVNC Server, which comes pre-installed on Raspberry Pi OS) is active and listening for connections. You can check its status and start it if needed from the Pi's desktop environment or via SSH. This is a very basic check, but it's often overlooked when people are trying to figure out why their access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working. It's like checking if the engine is on before trying to drive the car, in a way.
IP Address Woes
Your Raspberry Pi's internal IP address (like 192.168.1.100) needs to be stable. If your Pi's IP address changes regularly (which happens with "dynamic" IP addresses assigned by your router's DHCP server), your port forwarding rule will point to the wrong device. This is a classic problem. The solution is to give your Raspberry Pi a "static" IP address. You can do this either by configuring a static IP directly on the Pi or, more commonly and easily, by setting up a "DHCP reservation" in your router. This tells your router to always give the same IP address to your Pi, based on its unique MAC address. This is pretty important for consistent remote access, you see.
VNC Server Settings Check
The VNC server software itself has settings that can affect connectivity. For instance, some VNC servers might be configured to only accept connections from within the local network, or they might have specific security settings that are preventing external access. You should open the VNC Server application on your Raspberry Pi (usually found in the desktop menu under "Preferences" or "Internet") and check its options. Make sure it's set to allow connections and that any security features aren't overly restrictive for your intended use. It's also a good idea to ensure you're using the correct VNC display number (e.g., :0 or :1) when connecting, as this corresponds to the port number (5900 or 5901), which is something to keep in mind.
Firewall on the Pi
Just like your router, your Raspberry Pi can also have its own software firewall. If you've installed and enabled a firewall like UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your Pi, it might be blocking incoming VNC connections, even if your router is forwarding them correctly. You'll need to add a rule to your Pi's firewall to allow traffic on the VNC port (typically 5900 or 5901). You can do this via the command line. For UFW, it would be something like `sudo ufw allow 5900`. If you don't add this rule, your VNC connection will get to your Pi's doorstep but won't be allowed inside, which is another reason your access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working. It's a simple command, but very effective.
Client-Side Connection Problems
Sometimes, the issue isn't with your Pi or your home network at all, but with the computer you're trying to connect from. This is less common but still worth considering if all else fails, you know.
VNC Viewer Settings
The VNC viewer application on your remote computer needs to be configured correctly. Double-check that you're entering the right external IP address of your home network (or your DDNS hostname, if you're using one) and the correct port number. If you're using a non-standard external port (e.g., 20000) that forwards to 5900 on your Pi, you must specify that external port in your VNC viewer (e.g., `your.external.ip:20000`). Make sure there are no typos, as even a small mistake can prevent a connection. It's a bit like dialing the wrong phone number, really.
Local Network Firewall
The computer you're connecting *from* might also have a firewall that's blocking outgoing VNC connections. This is more common in corporate or public Wi-Fi networks that have strict security policies. If you're trying to connect from a work computer, for instance, its firewall might be preventing the connection. You might need to check your computer's firewall settings or try connecting from a different network, like a mobile hotspot, to rule this out. This is usually not the first thing to check, but it's a possibility, you know, especially if you're on a restricted network.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
While direct port forwarding for VNC can get you connected, it's generally not the most secure way to access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working, or working, for that matter. Opening ports on your router can expose your home network to potential risks. There are better, more secure methods that you should definitely consider, especially for long-term use. These methods add layers of protection, much like how a secure portal like Myaccess helps Floridians manage benefits online safely.
Why VPN is Safer
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your remote computer and your home network. Instead of opening a specific port for VNC, you connect to your home VPN server, and once connected, your remote computer acts as if it's physically on your home network. This means you can then connect to your Raspberry Pi via its internal IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.100) without any port forwarding for VNC. This is much more secure because only the VPN port needs to be open, and all traffic through the VPN tunnel is encrypted. It's a very robust way to get to your Pi, and it's something many people choose to do, actually.
Basic SSH Tunneling Setup
Another excellent and more secure option is to use an SSH tunnel. SSH (Secure Shell) is typically used for command-line access to your Pi, but it can also create a secure tunnel for other services, like VNC. You would port forward only the SSH port (default 22) on your router to your Raspberry Pi. Then, from your remote computer, you establish an SSH connection to your Pi and create a local port forward. This makes your VNC viewer connect to a local port on your remote computer, which then securely tunnels the VNC traffic through the SSH connection to your Pi. This way, the VNC port itself is never directly exposed to the internet, which is pretty clever, you know. It's a bit more involved to set up than simple port forwarding, but it offers a much higher level of security, and it's worth the effort, truly.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
When your access raspberry pi vnc over internet not working, it's best to follow a systematic approach. Don't just randomly change settings. Start with the basics and work your way outwards. This way, you can pinpoint the exact problem without getting too overwhelmed, which is pretty important.
Check Local VNC First
Before trying to connect from the internet, make sure VNC works when you're on the same local network as your Raspberry Pi. Connect your laptop or another computer to your home Wi-Fi and try to VNC to your Pi using its internal IP address (e.g., `192.168.1.100`). If this doesn't work, the problem is with your Pi's VNC server setup, not your internet connection or router. This is the first and most basic test, and it can save you a lot of time, you know.
Verify Pi's IP Address
On your Raspberry Pi, open a terminal and type `hostname -I` (that's a capital 'i'). This will show you its current internal IP address. Make sure this is the IP address you've used in your router's port forwarding settings. If it's different, you'll need to update your port forwarding rule or, better yet, set a static IP for your Pi as discussed earlier. This is a very common point of failure, actually.
Confirm VNC Server Status
Again, from the Raspberry Pi's terminal, you can check if the VNC server is running. For RealVNC Server, you might use a command like `sudo systemctl status vncserver-x11-serviced.service`. If it's not active, you can try starting it with `sudo systemctl start vncserver-x11-serviced.service`. Also, make sure it's enabled to start on boot: `sudo systemctl enable vncserver-x11-serviced.service`. This ensures that even after a reboot, your VNC server is ready to go, which is quite helpful.
Router Port Forwarding Walkthrough
Log into your router's web interface. Find the section for Port Forwarding, NAT, or Virtual Servers. Create a new rule:
- **Service Name:** Give it a name like "Raspberry Pi VNC."
- **Port Range (External/WAN Port):** This is the port you'll connect to from the internet. Use 5900 or 5901. If you're worried about ISP blocking or want more obscurity, pick a high, unused port like 20000.
- **Internal IP Address (LAN IP):** Enter your Raspberry Pi's static internal IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.100).
- **Internal Port (LAN Port):** This is the port the VNC server on your Pi listens on, typically 5900 or 5901.
- **Protocol:** Choose TCP (or sometimes TCP/UDP if available, but TCP is what VNC uses).
How to remotely access the Desktop of your Raspberry Pi over the
How to remotely access the Desktop of your Raspberry Pi over the
How to remotely access the Desktop of your Raspberry Pi over the